
Disinfection
To ensure water that enters a facility is free of pathogens and then remains free of pathogens throughout each facilities drinking water distribution system(s), viable measures of biosecurity must be employed. Within the public drinking water industry, these two areas of biosecurity are referred to respectively as Primary and Secondary Disinfection.
Primary Disinfection (Definition):
The treatment process element where a chemical and/or non-chemical disinfection process is
Used to achieve defined level of microbial inactivation and/or removal of pathogenic microorganisms from a given source water supply that satisfies the USEPA’s drinking water quality standards.
Secondary Disinfection (Definition)
There are a few pathogenic and potentially pathogenic bacteria that naturally occur in aquatic environments. Infecting their host they take opportunity of weakened defense mechanisms and hence are called an opportunistic microorganism. They typically inhabit surface waters or appear to grow in biofilms in water pipes causing regular problems in drinking water Distribution systems. (Krausset et al,2011) Likewise, secondary disinfection includes the application of a chemical disinfectant at the beginning, and at appropriate points along the water distribution network, to maintain a targeted residual disinfectant concentration throughout the system as a preventative measure from reverse contamination through water fixtures and for the eradication and prevention of biofilms within the water distribution system itself.
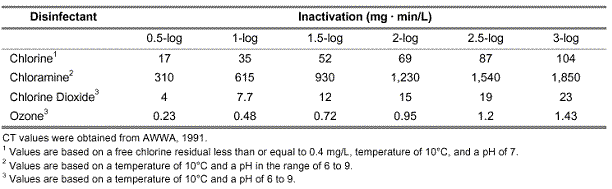
Furthermore, effective primary and secondary disinfection allow the disinfectant chemical to adequately mix in a contact tank. This adequate mixing has two purposes; one to make sure that all of the water that needs to be disinfected of microorganisms comes in contact with the disinfectant and, two that all of this water is in contact with the disinfectant for enough time for the disinfectant to do its job. This is made easier to figure out by looking at the CT (contact time) values for different disinfectants and planning accordingly. Figure 1 is a CT value chart for the inactivation of cryptosporidium with different antimicrobial agents.
Credit https://www.lenntech.com/library/ozone/comparison/ozone-disinfectants-comparison.htm
Helpful links
Paper on the biosecurity risk of groundwater
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/fe55/08297ec376ebb07950cbf7d981e6e3e60f30.pdf . Krausset et al, 2011